Welcome to Nafferton School’s arboretum.
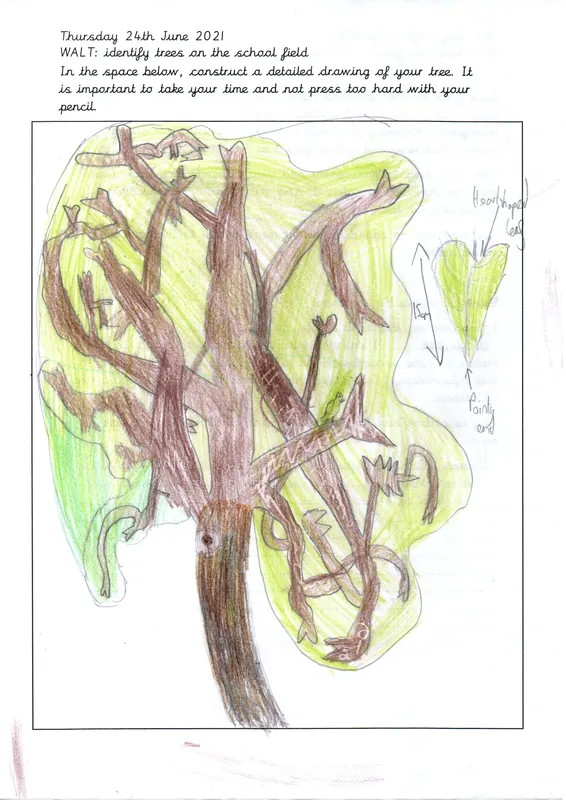
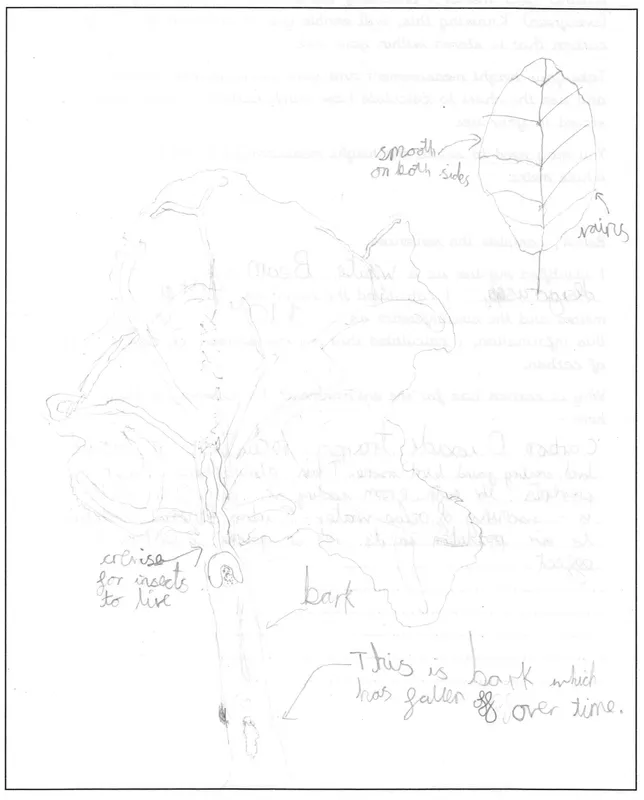
Here you will find information collected by the Y5 children in 2021 about the trees in the school grounds. The children selected trees around the Bray Way. They measured them and produced sketches of their shape, bark and leaf. Also, they calculated the height and how many kilograms of carbon was store within their chosen tree. They then researched information about their tree.
- What is an arboretum?
- An arboretum is a collection of trees. The trees are selected and grown to show a wide variety of different types – both native and non-native species.
Want to know how tall a tree is? How old it might be? Read on to find out…
Here Imogen explains how to work out the height of a tree using only a ruler.
‘It takes two people to do this, you will need a 30cm ruler and a piece of chalk. Your partner stands by the tree with the piece of chalk while you walk slowly backwards away from the tree, until the tree is the same length as the ruler. You have to close one eye to do that. Keeping one eye closed, your partner slowly raises their finger until you see it at the same height as 3cm on the ruler. You tell them to mark that point on the tree in chalk.
Then you have to measure the distance from the ground to the chalk mark and multiply that number by 10 to give you an approximate height.’
Here Gracie explains how to work out the circumference of a tree to calculate its age.
‘You need a piece of chalk and a tape measure. Measure from the ground to 130cm up the trunk and mark with the chalk. Repeat this on the opposite side of the tree. Then measure the circumference of the tree using the tape measure.’
The circumference can be used to calculate the approximate age of the tree.
Circumference ï¸ 2.5 = approximate age of the tree
(Oak and Beech are slow growing so using a calculator divide answer by 1.88)
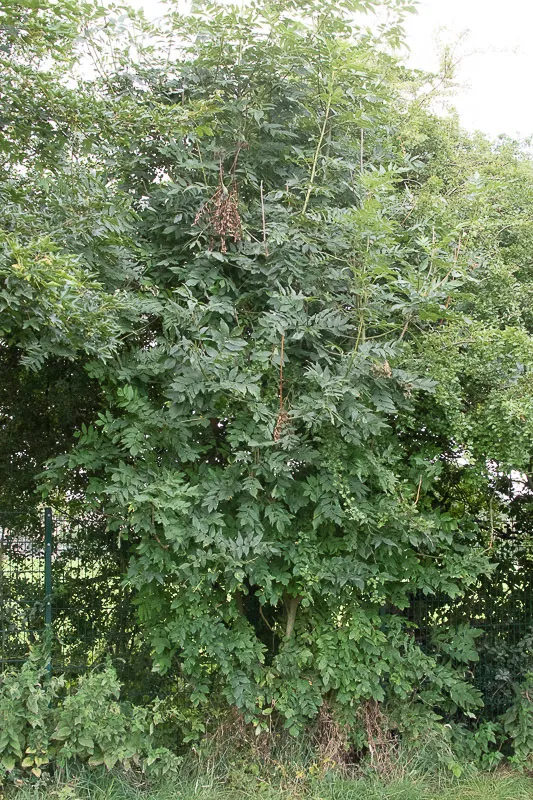

Scientific name: Fraxinus excelsior
Ash is native to the UK
Ash is one of the most common trees in the UK. It can grow 35 meters tall and can live for over 400 years. It can be identified by its black buds in twigs. Ash trees produce lots of winged fruits or ‘keys’ that form in bunches. They fall from the trees in winter and spring.
Ash is important to nature and provides a habitat for many species of insects and birds. Bullfinches eat the seeds and woodpeckers, owls, redstarts and nuthatches use the trees for nesting. Ash bark is often covered with lichens and mosses.
Ash has been affected by a fungus which causes "ash dieback". The disease has infected about 90% of Denmark's ash trees. In October 2012 ash dieback was found in mature woodland in Suffolk. It is thought that 80% of the ash trees in the UK will die.
Ash trees are in the olive family and produce oil that is chemically similar to olive oil.
Folklore: Yggdrasil, the World Tree in Viking mythology was an ash. It grew on an island surrounded by an ocean. This ash tree’s trunk reached up to the heavens, and its branches spread out over all the countries of the Earth. Its roots reached down into the Underworld. A squirrel ran up and down the tree carrying messages from the serpent gnawing at the roots to the eagle in the canopy. A deer fed on the ash leaves and from its antlers flowed the great rivers of the world.
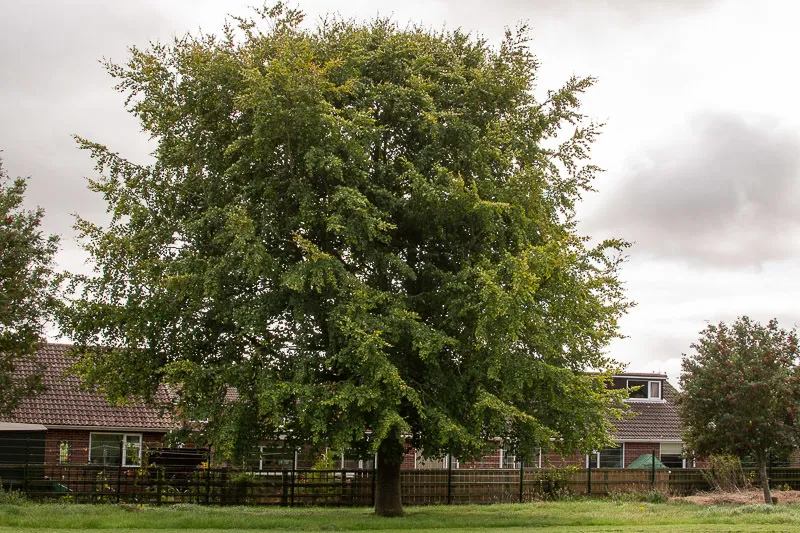



Scientific name: Fagus sylvatica
The Beech is native
Can grow up to 40 metres tall and is dome shaped. They have smooth grey bark and shiny leaves. They can live for 400 years. The Beech is wind pollinated and produces beech nuts as its seeds.
A beech woodland has a dense canopy which means it can be quite dark under it. There are some very rare plants that can grow there such as: box, bittercress and orchids. Moth caterpillars eat the leaves of the beech and mice, voles, squirrels and birds eat the beech nuts.
Leaves and bark of the tree contain pigments which were used in the past for dyeing fabrics. In some countries beech leaves were used instead of feathers as a stuffing for pillows.
Folklore: In Celtic mythology the beech tree was a symbol of a goddess; the partner to the oak and queen and mother of the woods. Beech groves were thought to be important to the ancient British Druids.


Scientific name: Ulmus
Elms are not native to the UK
There are several types of elm trees, they can grow up to 30 metres tall and can live for 100 years. Elms are not native to the UK and the English elm was probably brought over from Europe during the Bronze Age.
There used to be many more elms in the UK but during the 1960’s a disease called Dutch elm disease has killed millions of elm trees. The disease is a fungus that is carried by the elm bark beetle. Although called Dutch elm disease it came originally from Canada but was named after scientists from Netherlands who studied it.
Many birds and some small mammals eat elm seeds. The leaves provide food for the caterpillars of many moths.
Folklore: Elms were dedicated to Morpheus, the god of sleep. They used to also be associated with death, maybe because the trees can drop dead branches without warning. Elm wood was also the preferred choice for coffins.




Scientific name: Tilla
The Lime is native to the UK
Lime or Linden trees are deciduous trees. They can grow up to 40 metres and can live for 400 years.
There are three types of Lime in the UK, small-leaved, large-leaved and common. Common lime is a mix of small-leaved and large-leaved. They have heart shaped leaves and pale flowers.
Aphids love Limes and suck the sap turning it into honeydew, ants farm the aphids for this sweet treat. The leaves, when covered in honeydew, attract a lot of insects even though it is really aphid ‘poo’! The bark used to be used to make rope and the wood is still used today in furniture making as it does not warp. Vikings liked to make their shields out of Lime or Linden wood.
Limes are very important honey plants for beekeepers, producing a very pale but richly flavoured honey.
Folklore: Lime or Linden trees are associated with romance and lovers and the tree was often used as a symbol in romantic poetry. In France and Switzerland, limes represented freedom, and the trees were planted to celebrate battles.


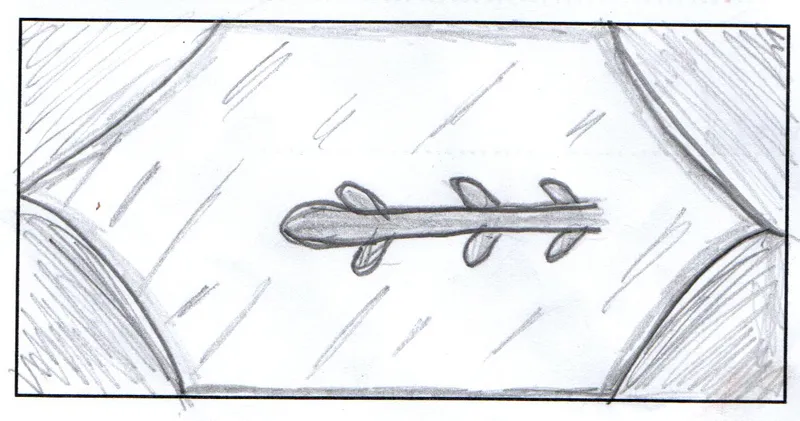
Scientific name: Acer campestre
Field maple is native to the UK
Field maples can grow to 20m and live for up to 350 years. The field maple is the UK’s only native maple. The leaves have five lobes and turn a beautiful golden colour in the autumn. Maples produce ‘helicopter’ seeds that spiral down from the tree in the autumn and are dispersed by the wind.
Ladybirds love maples as they are often home to many aphids, which they prey on. The flowers provide nectar for bees and small mammals eat the winged seeds.
Folklore: It was thought passing a child through the branches of a field maple would guarantee the child a long life. In some parts of Europe, it used to be thought that maple branches hung around a doorway stopped bats entering.
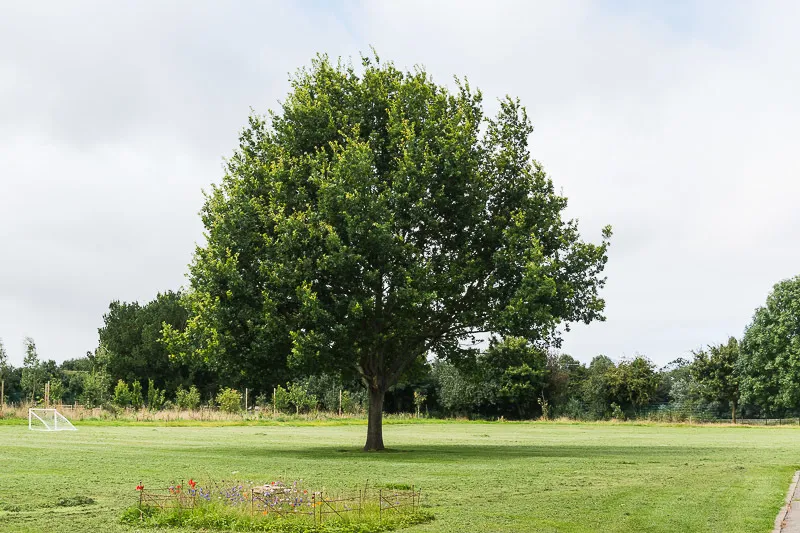




Scientific name: Quercus
The Oak is native to the UK
Oak is the most famous UK tree. Oak is a deciduous tree which means it loses its leaves in winter. There are several oak trees in the school grounds.
The English oak is the largest and most famous of the oak trees. Some oaks in England are more than 800 years old. A mature oak tree can be around 45 metres tall. It is a home for more animals than any other British tree. 30 species of birds, 45 different bugs and over 200 species of moth have been found on oaks. Beetles burrow under the bark, and some drill holes into the wood.
Wood of oak is very strong and hard. It is used to build of ships, furniture, floorings.
The fruit is the acorn—a round nut in a woody cup. New oaks can grow easily from acorns. Oaks produce more than 2000 acorns every year, but only one in 10 000 acorns will manage to develop into an oak tree.
Oak forests support more life than any other native forest. They are host to hundreds of insect species, supplying many birds with an important food source. In autumn, mammals such as squirrels, badgers and deer feed on acorns.
The large round growths found on the trunks of oak trees, caused by a species of gall wasp, were used to make ink for over a thousand years, right through to the 20th century.
Folklore: a branch of oak was considered to have special powers, as was any mistletoe found growing on an oak tree. Carrying an acorn guarded against disease and promoted long life, while planting an acorn at the time of a new moon was said to bring wealth. If an acorn was placed in a window, it was believed to protect the house from a lightning strike.
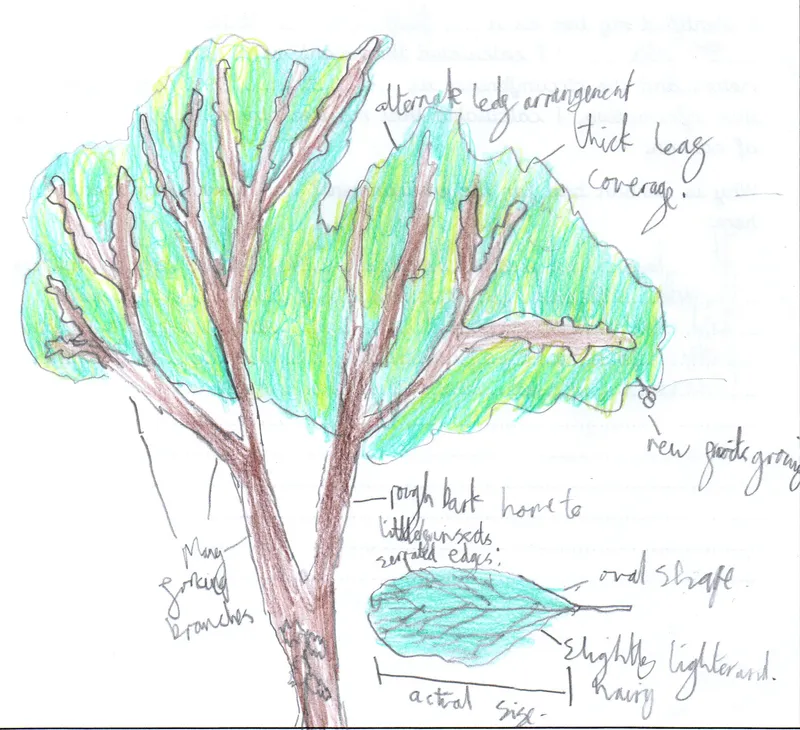
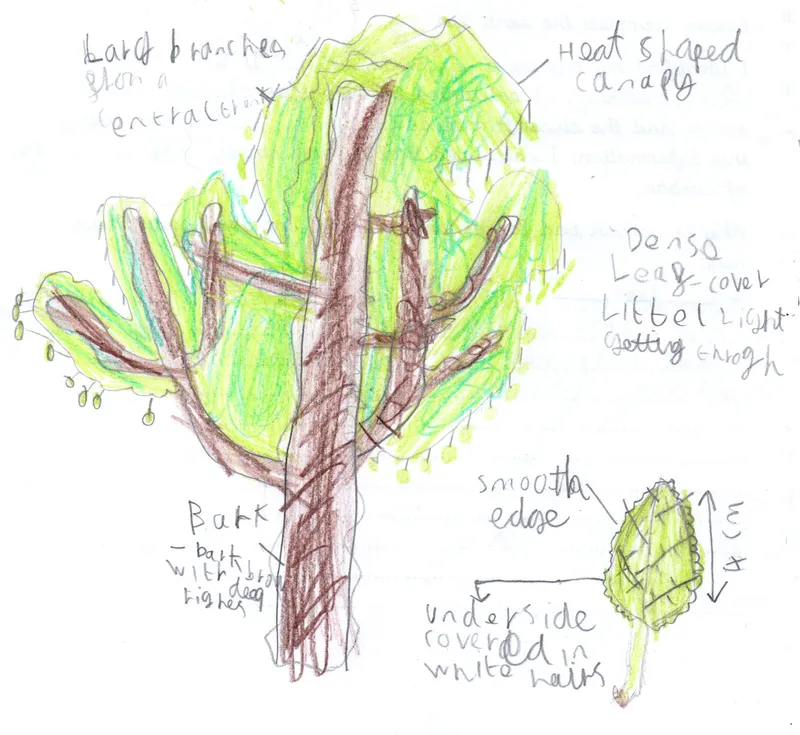
Scientific name: Prunus domestica
Plum is not native to the UK
A small tree growing to 12 meters and short-lived in tree terms. It has beautiful blossom in the spring and tasty plums in the autumn. Plums grow in every continent of the world except Antarctica. It is thought it was the first fruit tree to be planted for food by Neolithic people. Like most fruit, plums are low in calories, protein and fats.
Lots of animals, birds and insects feed on the plum. Its flowers are very important to many insects including honey bees.
Folklore: The fruit of the wild plum is associated with endurance and the vitality of life. It is a particularly important symbol in Chinese culture.
Enter text...
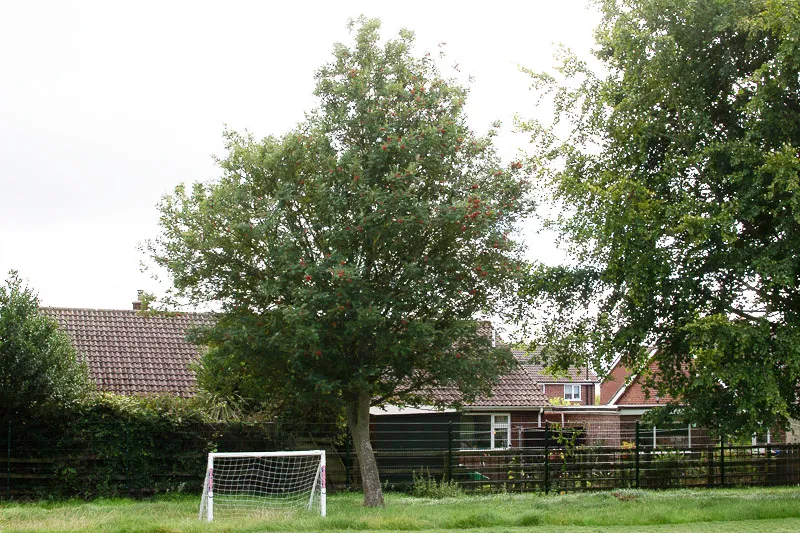
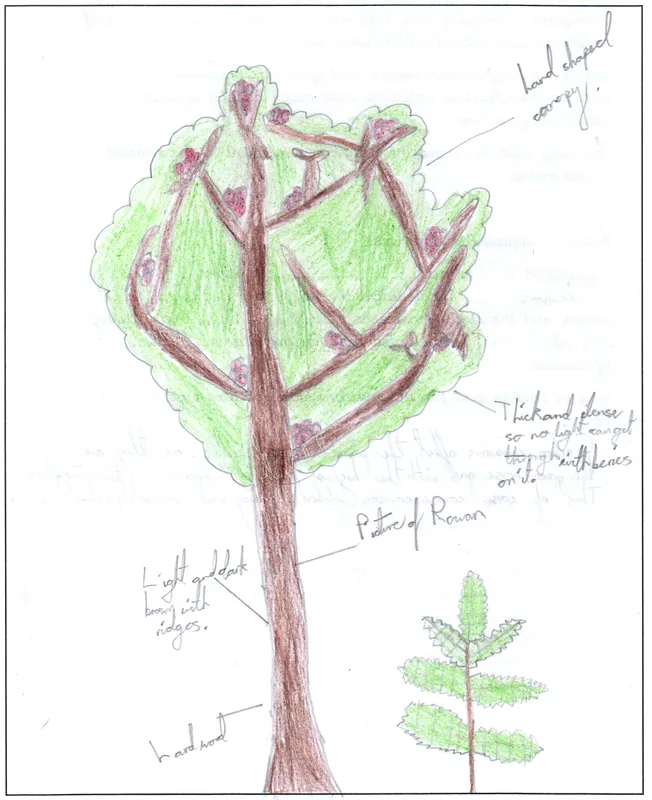


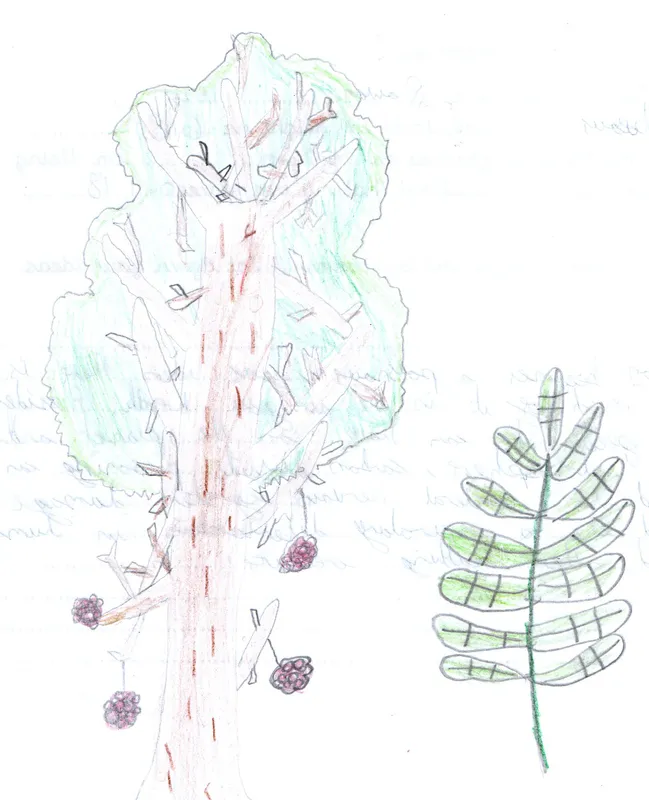
Rowan also known as mountain ash
Scientific name: Sorbus caucuparia
The Rowan is native
Mature trees can grow to 15m in height and can live for up to 200 years. They have beautiful bunches of red berries in the summer and autumn. There are several Rowan’s in the school grounds. Native to cooler regions of the northern hemisphere and is most common in the UK in the north and west, it often grows in high-altitude locations.
The leaves are eaten by the caterpillars of a number of moths. Caterpillars of the apple fruit moth feed on the berries.
Flowers provide pollen and nectar for bees and other pollinating insects. Blackbirds, thrushes, redwings, fieldfares and waxwings like to eat the juicy fruit of rowan. They play important role in dispersal of its seed.
Rowan is a rich source of vitamin C. It has sour taste and can be used in of jellies, jams and preserves.
Rowan is also known as the mountain ash due to the fact that it grows well at high altitudes and its leaves are similar to those of ash.
Folklore: Rowan was once widely planted near houses as a protection against witches. The colour red was considered to be the best colour for fighting evil, and so the rowan’s bright red berries have been associated with magic and witches.
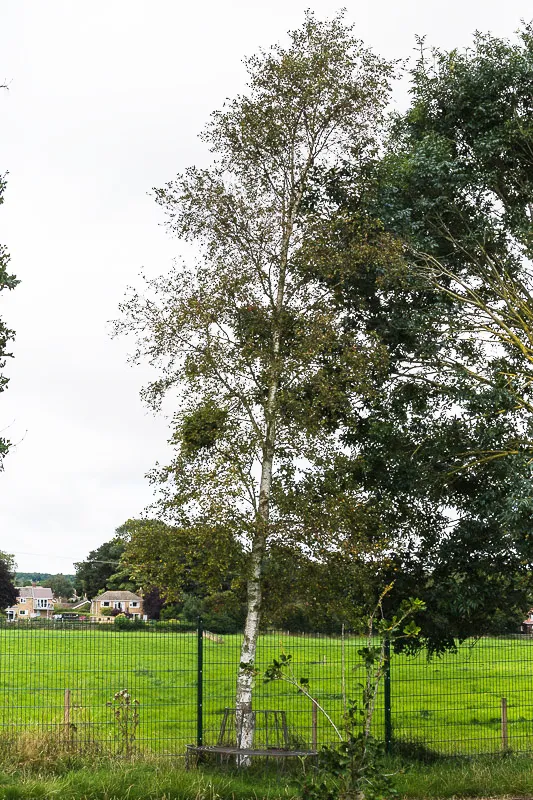


Scientific name: Betula pendula
Silver Birch is native to the UK
A silver birch can grow up to 30 meters and has a white/silver bark from where it gets its name. The yellow flowers of the silver birch are called catkins and appear in the spring.
Silver birch provides food and habitat for more than 300 insect species – the leaves attract aphids which provide food for ladybirds and other species further up the food chain. The leaves are also a food plant for the caterpillars of many moths.
Folklore: In Celtic mythology, the birch symbolised renewal and purification. Bundles of birch twigs were used to drive out the spirits of the old year. It was also used as a symbol of love and fertility. In Scottish Highland folklore, a barren cow herded with a birch stick would become fertile, and a pregnant cow would bear a healthy calf.
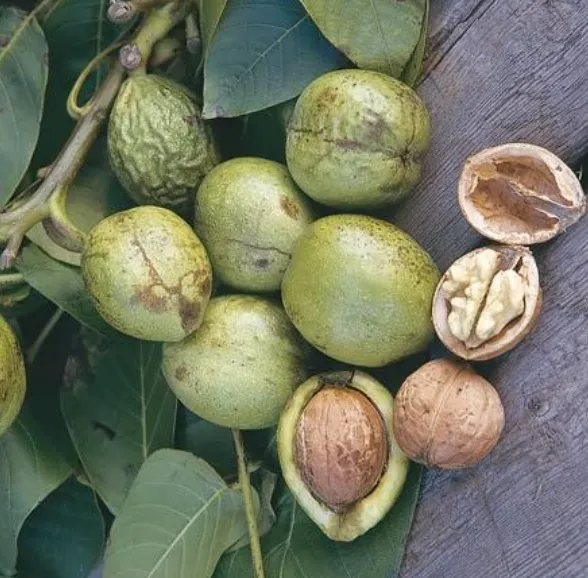
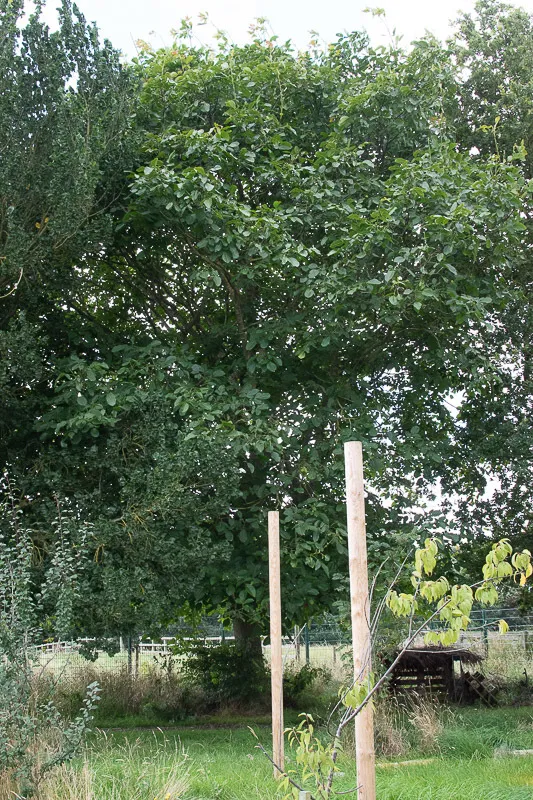



Scientific name: Juglans regia
Walnuts are not native to the UK
This tree can grow to 35 meters high and can live for 200 years. It is not native to the UK and was brought over by the Romans. It came from southern Europe and central Asia. It produces walnuts, which some people are allergic to and so our walnut tree is marked with a red ribbon to let everyone know.
Many animals, particularly mice and squirrels, will eat the walnut seeds as they are high in nutrients and fats. Some caterpillars will eat the leaves of the tree.
Walnut trees have a strong and deep taproot which produces a chemical to stop other plants growing nearby.
Folklore: The walnut's scientific name, Juglans, comes from Roman mythology. According to an ancient myth, Jupiter, who was also known as Jove, dined on walnuts when he lived on earth. Therefore, Romans called walnuts Jovis glans, meaning 'the nuts from Jupiter’.
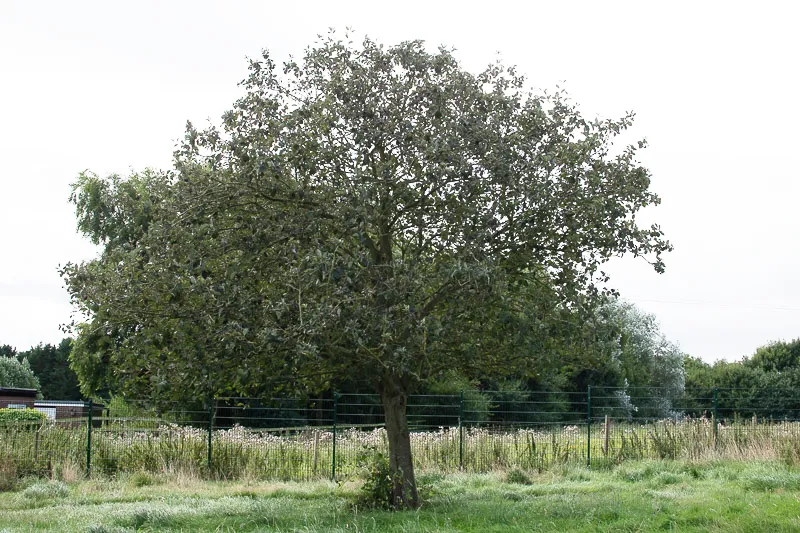



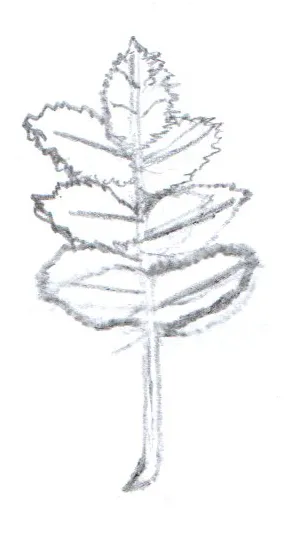
Scientific name: Sorbus aria
The Whitebeam is native to the UK
Whitebeam is a smaller tree, growing up to 15 meters in height. It is deciduous which means it drops its leaves in the winter. The leaves have soft white hair on the underneath and that is where it gets its name from. It has pretty white flowers in the spring and red berries in the autumn. They live 70-80 years.
The flowers are pollinated by insects and birds like to eat the berries. The leaves are eaten by several types of moth caterpillars.
Folklore: The Anglo Saxons used whitebeams as boundary markers. Myths and legends use the tree to both conjure and repel magic and it was used to make wands.










